At Topmetalstamping, a precision-focused manufacturer and factory serving global OEMs and industrial suppliers, we’re often asked one core machining question: What’s the real difference between CNC milling and CNC drilling—and which one is right for my part?
Both processes are essential in CNC manufacturing, but they serve very different purposes in terms of geometry, flexibility, cost, and performance. Understanding these differences helps you choose the most efficient, high-quality solution for your project—especially when custom service and tight tolerances are involved.
Let’s break it down in a clear, practical way.
What Are the Basic Concepts and Differences Between Drilling and Milling?
At a high level, CNC drilling and CNC milling differ in tool movement, cutting capability, and application scope.
CNC Drilling: The Fundamentals
CNC drilling is a machining process dedicated to producing round holes. The drill bit rotates on its axis and moves vertically (along the Z-axis) into the material. The tool does not cut laterally.
Key characteristics:
- Single-purpose operation
- Straight, round holes only
- High speed and efficiency
- Minimal toolpath complexity
Drilling is ideal when hole location and diameter matter—but shape complexity does not.
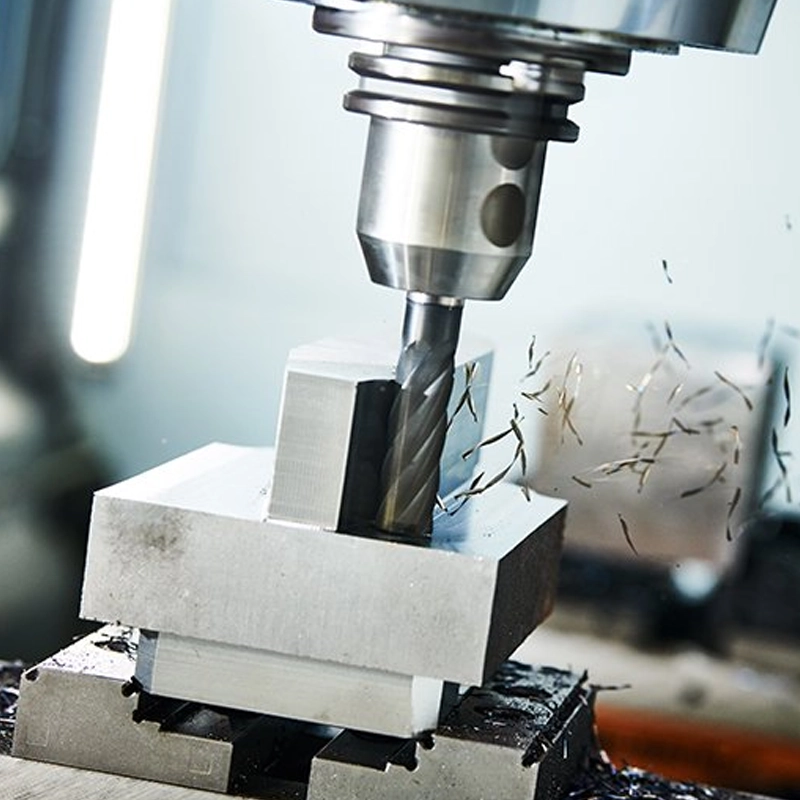

CNC Milling: The Fundamentals
CNC milling uses rotating cutting tools that move along multiple axes (X, Y, and Z). This allows the tool to remove material from the surface, edges, and interior of a workpiece.
Key characteristics:
- Multi-axis cutting capability
- Can create slots, pockets, contours, and complex 3D shapes
- Supports a wide range of tools and operations
- Highly adaptable for custom parts
Milling is the go-to process for parts requiring geometry beyond simple holes.

How Does Milling Technology Work in CNC Manufacturing?
CNC milling machines remove material by combining tool rotation with programmed linear and circular movements. Modern mills can operate in 3-axis, 4-axis, or 5-axis configurations, enabling complex machining in a single setup.
Key Milling Operations
Common CNC milling operations include:
- Face milling
- End milling
- Slotting
- Pocketing
- Contouring
- Thread milling
These operations make milling extremely versatile, especially for custom service projects that require precise features or frequent design changes.

Comparison Table: CNC Drilling vs. CNC Milling
| Feature | CNC Drilling | CNC Milling |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Creating holes | Shaping and cutting surfaces |
| Tool Movement | Z-axis only | X, Y, and Z axes |
| Geometry Capability | Round holes | Complex 2D and 3D features |
| Efficiency | Very high for holes | Moderate to high |
| Flexibility | Low | Very high |
| Typical Cost | Lower | Higher |
What Is Drilling Technology and How Is It Applied?
Drilling technology focuses on speed, repeatability, and accuracy for hole-making operations. CNC drilling machines or drilling cycles on machining centers are optimized for fast production and consistent results.
Common Applications of CNC Drilling
CNC drilling is widely used in:
- Metal brackets and plates
- Automotive components
- Electronics housings
- Sheet metal parts
- Structural components
For parts requiring many identical holes, drilling is often the most cost-effective and high-quality solution.
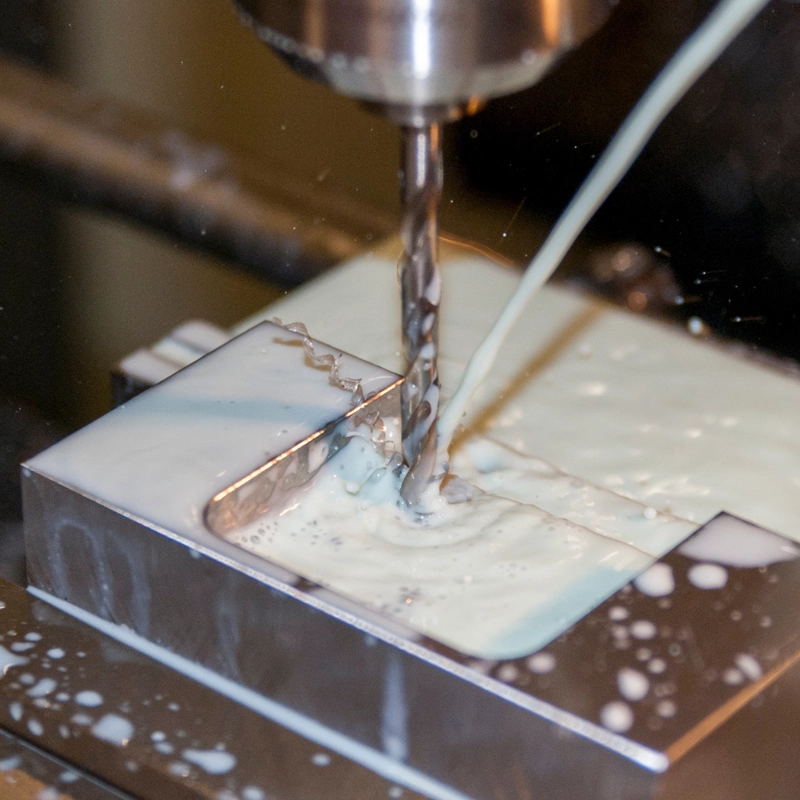

How Do Milling and Drilling Compare in CNC Machining?
In practice, drilling and milling are often used together in a single CNC program. A part may be drilled for mounting holes and then milled for pockets, edges, or profiles.
Key comparison points:
- Complexity: Milling supports complex shapes; drilling does not
- Speed: Drilling is faster for hole-only tasks
- Cost: Drilling is typically cheaper; milling adds value through functionality
- Customization: Milling excels in custom and low-to-medium volume production
At Topmetalstamping, we often recommend a hybrid approach to balance performance and cost.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Milling vs. Drilling?
CNC Drilling: Focused and Efficient
Advantages
- Fast cycle times
- Lower tooling and programming costs
- Excellent repeatability for holes
Disadvantages
- Limited to round holes
- No surface shaping capability
- Less flexibility for design changes

CNC Milling: Versatile and Capable
Advantages
- Supports complex geometries
- High precision and surface finish
- Ideal for custom service and prototyping
Disadvantages
- Higher machine and tooling costs
- Longer setup and machining times
- Requires advanced programming
How to Choose Between Milling and Drilling for Your Project?
Choosing the right process depends on part design, volume, and performance requirements.
Choose CNC Drilling When:
- Your part only needs round holes
- Hole quantity is high and geometry is simple
- Cost and speed are top priorities
Choose CNC Milling When:
- Your part has complex shapes or profiles
- Tight tolerances and surface finish matter
- You need design flexibility or customization
A reliable manufacturer will help evaluate these factors early to avoid unnecessary cost or redesign.

Conclusion
CNC milling and CNC drilling are not competing processes—they’re complementary tools in modern manufacturing. Drilling delivers speed and efficiency for hole-making, while milling provides unmatched flexibility and geometric control.
At Topmetalstamping, we support customers as a trusted factory and manufacturer, offering high-quality, precision CNC solutions tailored through our custom service approach. Whether you’re sourcing from global suppliers or developing a new design, our engineering team is ready to help you choose the most efficient machining strategy.
Not sure which process fits your part best?
Looking for a reliable partner for custom CNC machining?
Contact Topmetalstamping today to discuss your project, request a technical review, or get a competitive quote. We’re always happy to collaborate and help you build better parts.