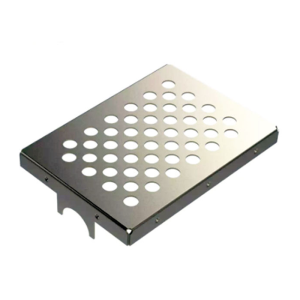
When it comes to manufacturing electronics enclosures, selecting the right metal stamping method can be the difference between a successful product and a costly mistake. Whether you’re designing enclosures for consumer electronics, medical devices, or industrial machinery, the choice of stamping technique impacts production costs, quality, and speed. This decision is not only about picking a process that suits your design but also one that optimizes production efficiency, ensures high-quality results, and meets budget constraints.
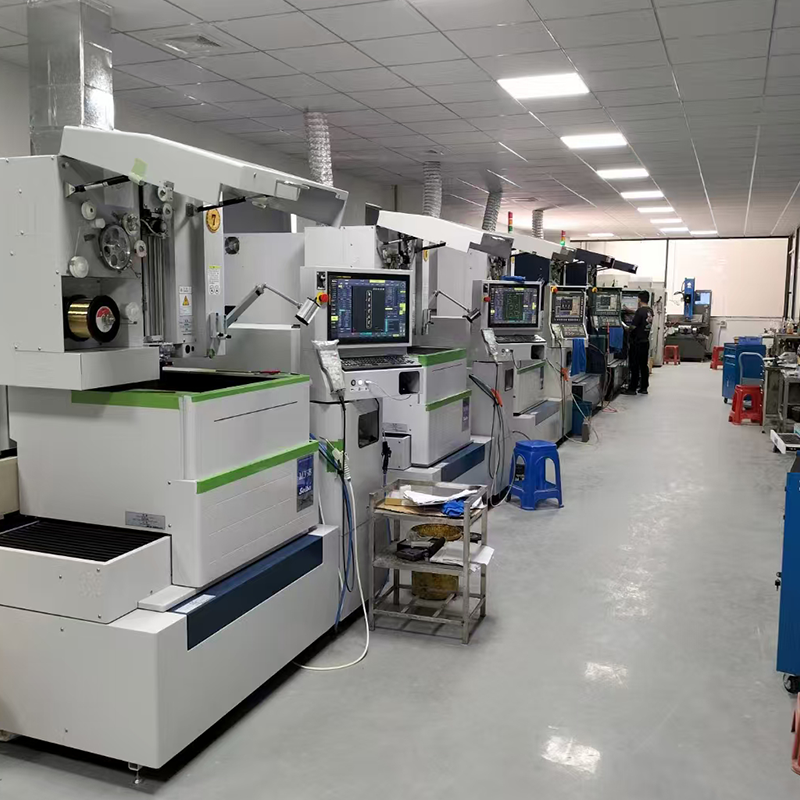

At Topmetalstamping, we specialize in providing high-quality custom metal stamping solutions that cater to the unique needs of our clients. We understand that every project is different, and our team of experts works closely with you to choose the best stamping method, material, and finishing processes for your specific application. In this blog, we’ll guide you through the most common metal stamping methods, help you choose the right one for your electronics enclosure project, and explain how the materials used in stamping play a critical role in ensuring long-lasting protection for your electronic components.
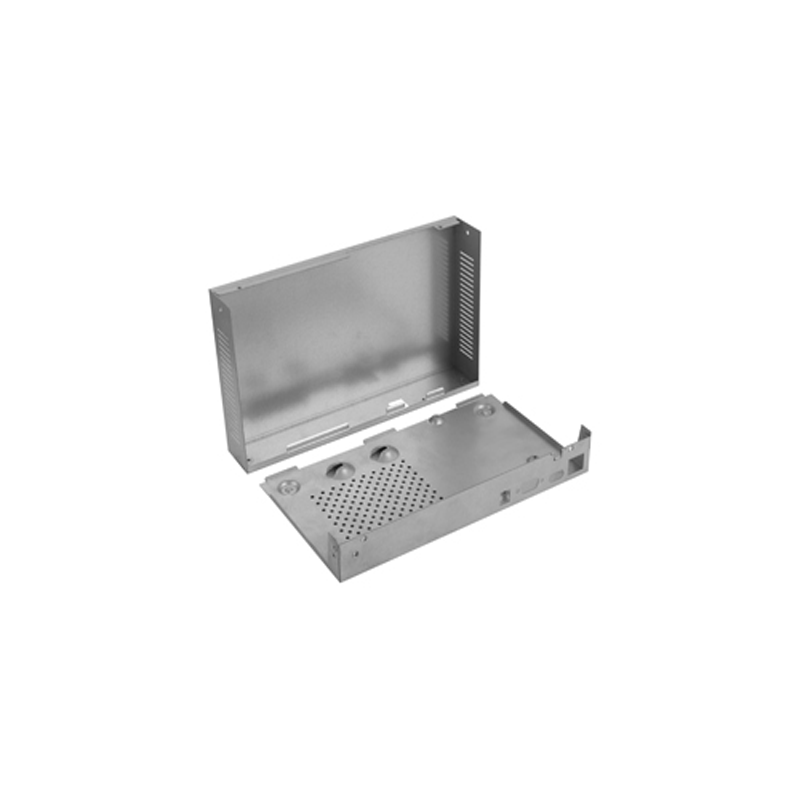

Understanding Metal Stamping Methods for Electronics Enclosures
The metal stamping process is the technique of using molds and dies to shape metal sheets or coils into desired forms. For electronics enclosures, this method is often the most efficient and cost-effective way to produce high-quality, durable components. Different stamping techniques cater to specific enclosure designs and production needs. Below are the most commonly used metal stamping methods in the electronics industry:
1. Progressive Die Stamping
Progressive die stamping is a high-speed, high-volume method commonly used for manufacturing electronic enclosures that have complex features like holes, bends, and slots. This method works by feeding a coil of metal through a series of dies, each performing a different operation (cutting, bending, punching) as the material moves through the press. It’s an ideal method for mass production because it minimizes material waste and significantly reduces cycle times.
- Best For: High-volume production of complex, flat parts with multiple operations.
- Advantages: Extremely fast, minimal waste, cost-effective for high-volume production.
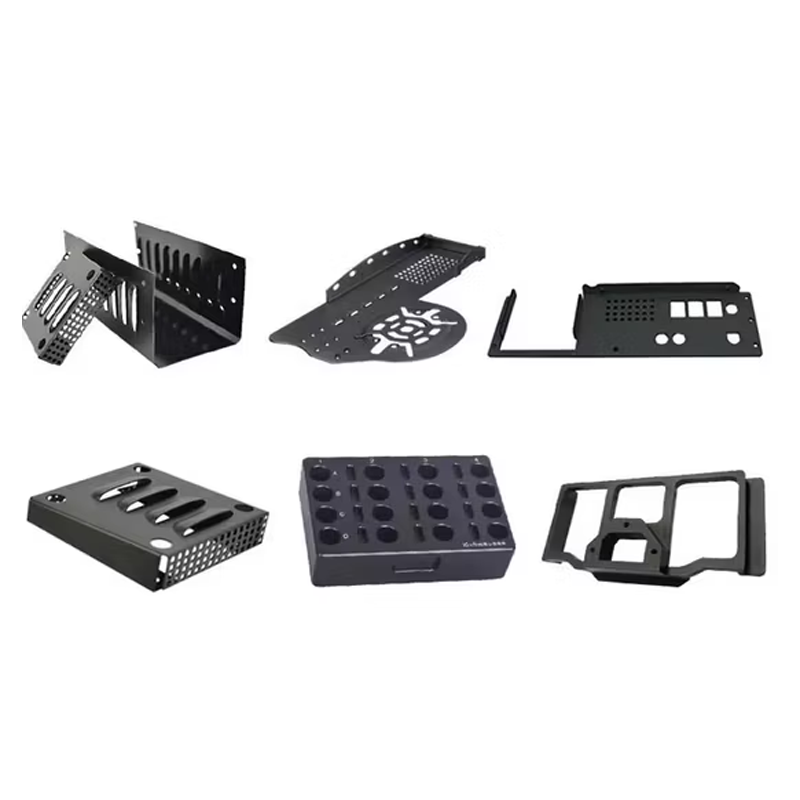

2. Fourslide Stamping
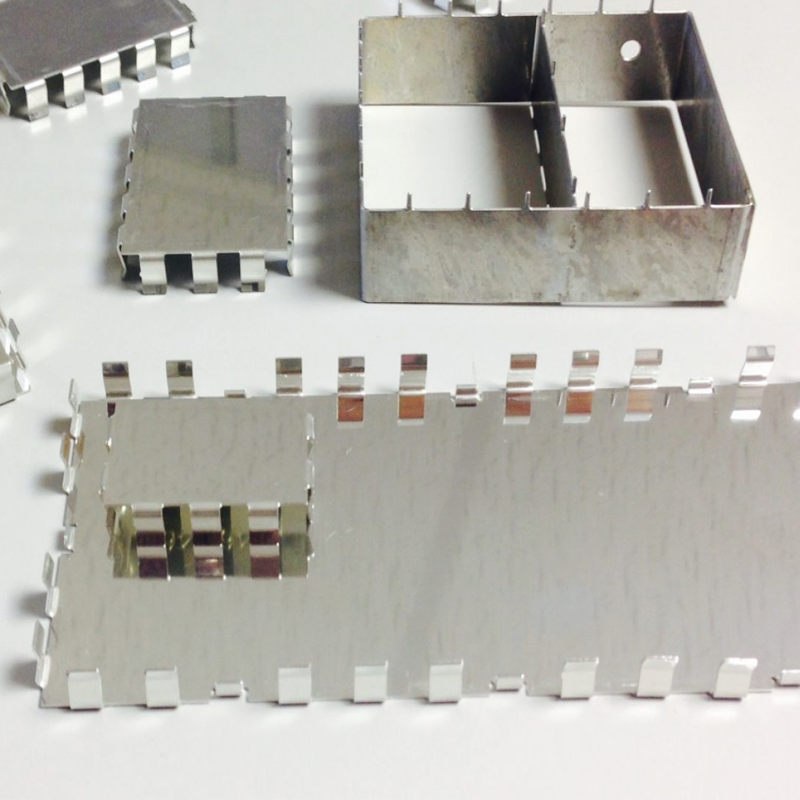
Fourslide stamping, also known as multislide stamping, is ideal for parts that require multiple, complex bends or shapes. Unlike progressive die stamping, which uses a single vertical ram, fourslide stamping uses four sliding tools to form the part from different directions. This method is particularly useful for creating clips, terminals, and brackets for electronic enclosures that need intricate designs and tight tolerances.
- Best For: Parts with multiple or complex bends (clips, terminals).
- Advantages: Precision in parts with complicated geometries, high flexibility in design.
3. Deep Draw Stamping
If your electronics enclosure needs to be shaped like a can or a box, deep draw stamping is the method of choice. This process involves punching a flat metal sheet into a die cavity, forming a three-dimensional shape. The depth of the enclosure is greater than its diameter, making it perfect for seamless, durable enclosures that provide excellent protection for sensitive electronic components.
- Best For: Seamless, deep, cup-shaped, or box-shaped enclosures.
- Advantages: Excellent for creating strong, seamless, and durable enclosures.
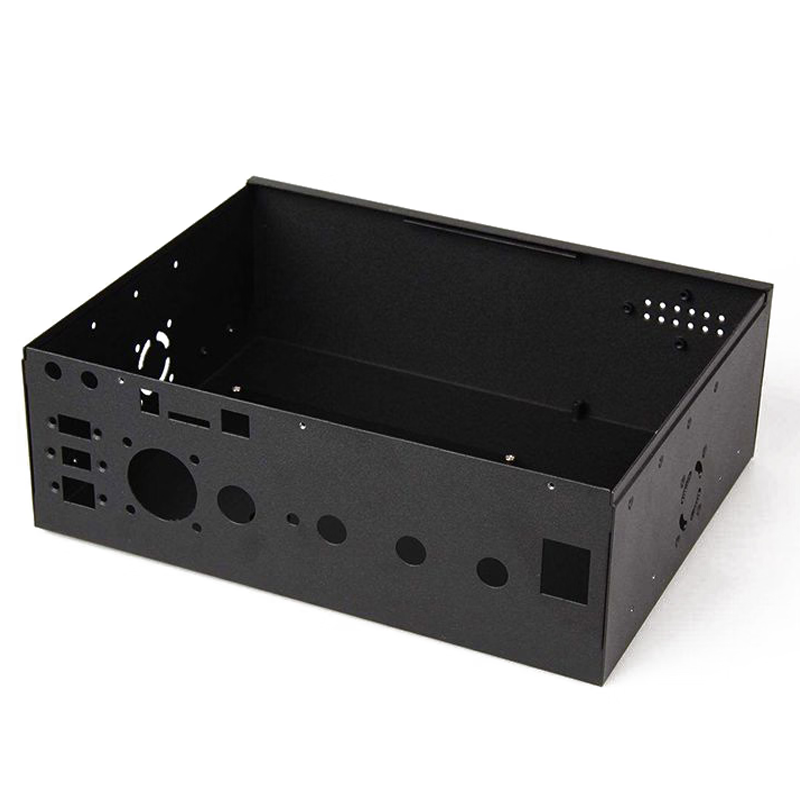

4. Compound Die Stamping
Compound die stamping involves a single die that performs two or more operations simultaneously. This method is best suited for producing simple, flat parts like washers, blanks, and small enclosures that don’t require intricate shapes. Compound die stamping is a cost-effective choice for low- to medium-volume production runs.
- Best For: Simple, flat parts (washers, blanks).
- Advantages: Cost-effective for simple parts, lower tooling costs.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Electronics Enclosure
Selecting the right material is crucial to ensuring that your electronics enclosures provide optimal protection and meet the functional requirements of your project. Each material has its own set of properties, such as strength, corrosion resistance, weight, and conductivity, that can significantly impact the performance and longevity of your enclosure.
Common Materials for Metal Stamping
- Steel: Steel is the most commonly used material for electronic enclosures because of its strength and low cost. For general-purpose applications, cold-rolled steel is often used. Stainless steel is ideal when corrosion resistance is required, making it an excellent choice for outdoor or harsh environments.
- Aluminum: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and offers good thermal conductivity, which helps dissipate heat from electronics. It’s the ideal choice when weight is a concern, especially for portable devices.
- Copper & Brass: When you need excellent electrical conductivity and shielding for electromagnetic interference (EMI), copper and brass are the best options. These materials are used in enclosures that require high conductivity for electrical components.
- Other Specialized Materials: Depending on your needs, we can work with other materials like zinc or magnesium alloys for specific properties like heat resistance, or to meet unique electrical and chemical requirements.
Material Selection Guide
| Material | Cost | Weight | Strength | Corrosion Resistance | Conductivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cold Rolled Steel | Low | Heavy | High | Poor | Poor |
| Stainless Steel | Medium | Heavy | High | Excellent | Poor |
| Aluminum | Medium | Light | Medium | Good | Good |
| Copper/Brass | High | Heavy | Medium | Good | Excellent |
At Topmetalstamping, we assist our customers in selecting the best material based on their specific project requirements, ensuring that the final product meets functional, environmental, and aesthetic needs.
The Metal Stamping Process: Steps to Success
Understanding the metal stamping process from start to finish is essential for ensuring that your electronics enclosures meet quality standards and are delivered on time. Below are the seven key steps involved in the stamping process at Topmetalstamping:
- Design & Engineering Review: Before starting production, our engineers review your 3D CAD files to ensure the design is manufacturable and optimized for stamping.
- Tool & Die Design and Fabrication: We create custom tools (dies) that will form your part. This step is crucial, as the quality of the tooling determines the quality of the final product.
- Material Selection & Preparation: Based on your specifications, we select the right material and prepare it for the stamping process.
- Stamping Press Setup: Our technicians calibrate the press to match the material and complexity of the part.
- Stamping Production Run: The stamping press performs the stamping operation, producing parts at high speed.
- Secondary Operations: After stamping, parts may undergo additional processes such as deburring, plating, or powder coating.
- Quality Inspection & Packaging: Every part undergoes a thorough inspection to ensure it meets your tolerances and quality standards before being packaged for delivery.
Conclusion
Selecting the right metal stamping method, material, and process is critical for producing high-quality, cost-effective electronics enclosures. Whether you are creating enclosures for consumer electronics, medical devices, or industrial machinery, Topmetalstamping offers expert guidance to help you navigate this process. Our team ensures that every part is crafted with precision, using the most efficient methods to meet your project’s timeline and budget.
For more information about how we can help with your next project, or to request a custom quote, reach out to us today. We offer a full range of OEM services, providing high-quality, custom metal stamping solutions tailored to your needs. Let Topmetalstamping be your trusted partner for all your electronics enclosure needs.