In the world of modern manufacturing, precision and efficiency are paramount. One of the most powerful tools in achieving these qualities is laser cutting, a technology that utilizes a high-powered, focused beam of light to cut, melt, or vaporize materials with exceptional accuracy. Whether you’re working in industries like aerospace, automotive, electronics, or signage, laser cutting has become a go-to solution for producing complex shapes with minimal waste and maximum quality.
At Topmetalstamping, a leading supplier and manufacturer based in China, we understand that laser cutting is more than just a process—it’s an essential part of creating high-quality, efficient, and cost-effective components. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down how laser cutting works, its key components, the materials it can process, the different types of lasers available, and how it compares to other cutting methods. By the end of this blog, you’ll have a clear understanding of why laser cutting is a vital part of modern manufacturing and how it can benefit your business.
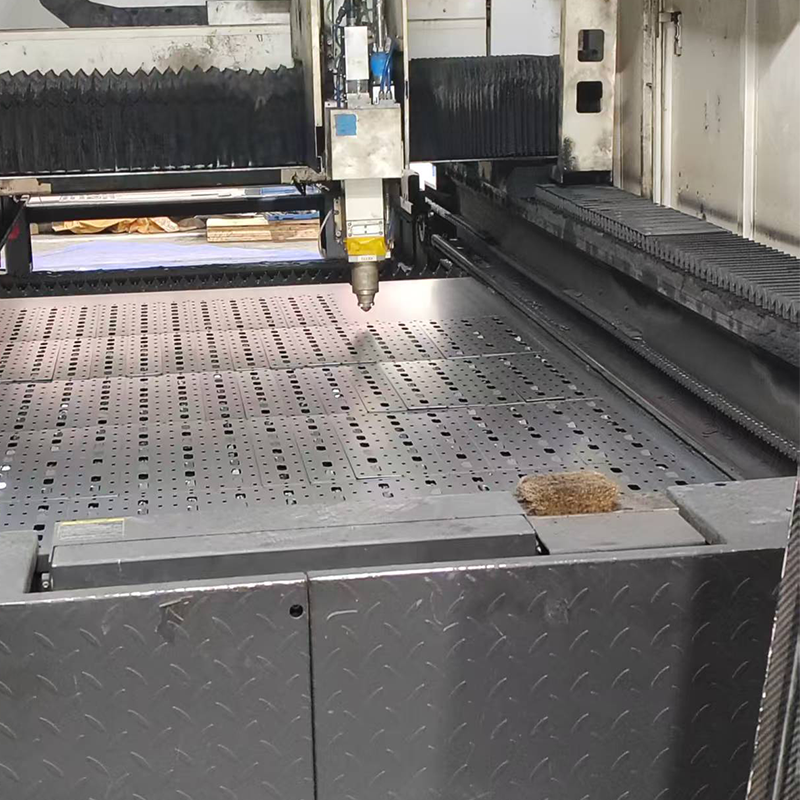

What Is Laser Cutting?
Laser cutting is a non-contact fabrication process that uses a highly focused laser beam to cut, melt, or vaporize materials with extreme precision. The laser generates a significant amount of heat, allowing it to cut through materials like metals, plastics, wood, and ceramics with minimal mechanical force. One of the biggest advantages of laser cutting is that it produces clean cuts with fine details, reducing the need for secondary processes like sanding or polishing.
At Topmetalstamping, we rely on advanced laser cutting systems to provide custom solutions for a wide range of industries, ensuring fast, high-quality production while minimizing waste.
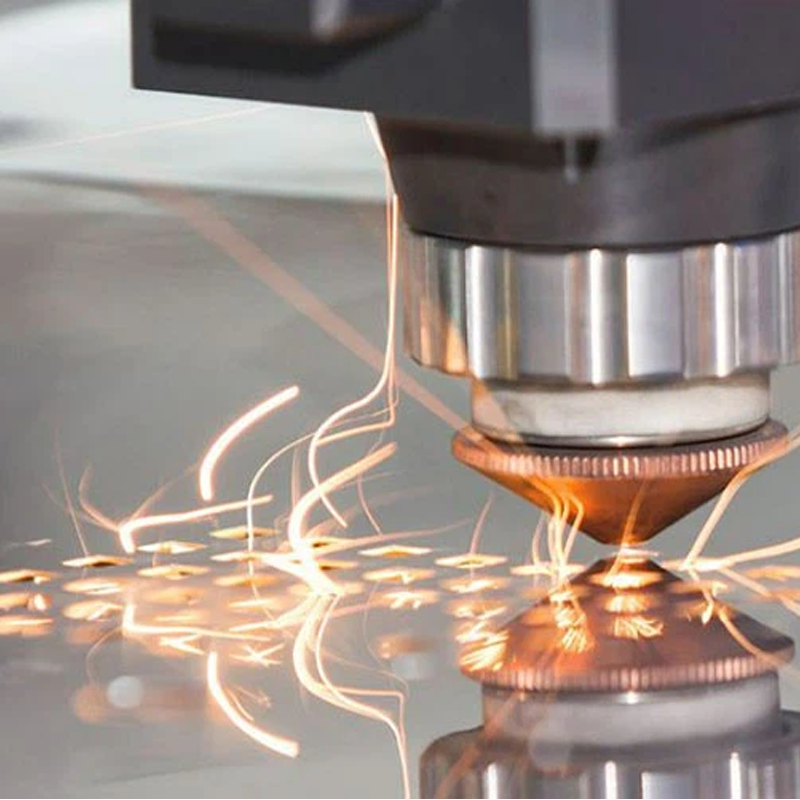

How Does Laser Cutting Work?
The laser cutting process is relatively straightforward but involves several critical steps:
- Laser Beam Generation: The process begins with the generation of a powerful laser beam. This can be done using various sources, such as CO₂ gas tubes, fiber lasers, or solid-state lasers like Nd:YAG. The type of laser used depends on the material being cut and the precision required for the job.
- Beam Focusing: Once the laser is generated, the beam is directed through a series of mirrors or fiber optics to a cutting head, where it is focused to a small point—usually less than 0.2 mm in diameter. This focusing increases the energy density, enabling the beam to melt or vaporize the material.
- Material Interaction: When the laser beam interacts with the material, the heat causes it to melt, burn, or vaporize. This results in a clean, narrow cut, known as the kerf, with minimal distortion or burr formation.
- Assist Gas Application: During the cutting process, assist gases such as nitrogen, oxygen, or compressed air are used to blow away molten material and debris, help cool the cutting area, and sometimes influence the chemical reaction (e.g., oxidizing metals like steel). The choice of gas depends on the material being cut and the desired quality of the cut edge.
- CNC Motion Control: The final step involves the movement of the cutting head or the workpiece itself. This is controlled by a CNC (Computer Numerical Control) system, which allows for highly precise movements along digital toolpaths defined by CAD/CAM software. This automation ensures that the cuts are accurate and repeatable, even in complex designs.
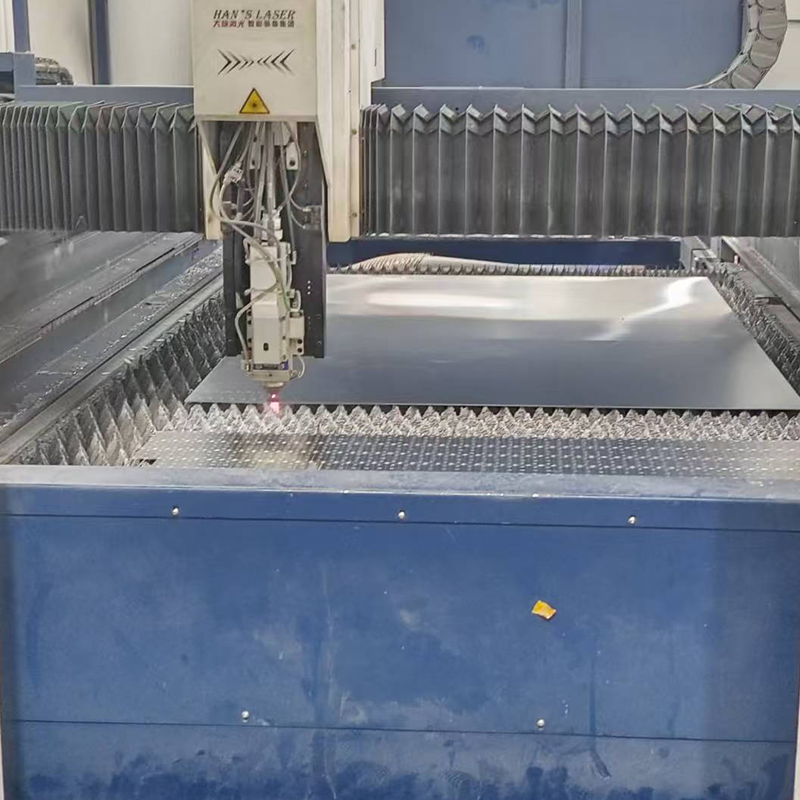

Key Components of a Laser Cutting Machine
A typical laser cutting machine consists of several integrated components working together to create high-precision cuts. These include:
- Laser Resonator: Generates the laser beam using a laser medium like CO₂ gas or fiber. It defines the power, wavelength, and cutting capability of the system.
- Beam Delivery System: Transports the laser beam from the resonator to the cutting head via mirrors or fiber-optic cables.
- Focusing Lens: Focuses the laser into a narrow point, increasing its energy density for effective cutting.
- Cutting Head: Houses the lens and nozzle, controlling the position of the laser beam on the material.
- Motion Control System: Uses CNC to move the cutting head or workpiece accurately along predefined paths.
- Assist Gas System: Delivers gases like nitrogen, oxygen, or compressed air to the cutting zone, improving cut quality.
- Cooling System: Ensures that the laser components do not overheat during use.
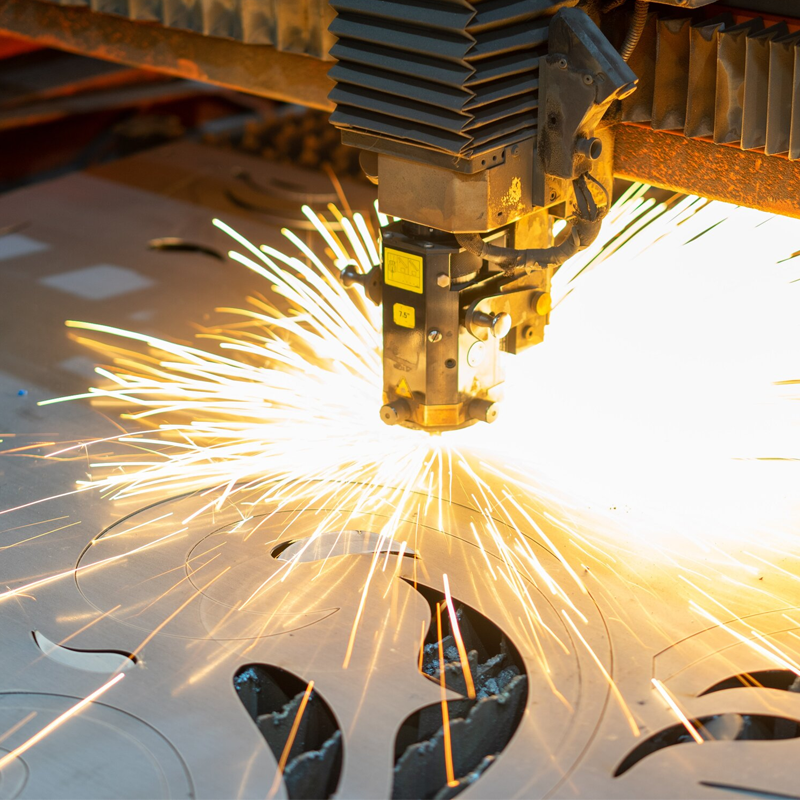

Types of Lasers Used in Laser Cutting
The type of laser used depends on the materials to be cut and the required precision. The most common types of lasers include:
- CO₂ Lasers: Best suited for cutting non-metals like wood, acrylic, and plastics. CO₂ lasers offer excellent performance on organic and non-metal materials, though their efficiency on reflective metals is lower.
- Fiber Lasers: Highly efficient and capable of cutting reflective metals like stainless steel, aluminum, and brass. Fiber lasers offer high cutting speeds and low maintenance, making them ideal for metalworking applications.
- Nd:YAG Lasers: Used for cutting metals, ceramics, and plastics. Nd:YAG lasers have high power density, making them suitable for thicker materials but requiring more maintenance.
- Excimer Lasers: These lasers use ultraviolet (UV) light for “cold” cutting, which minimizes heat damage. They are primarily used for delicate tasks such as microelectronics and medical device manufacturing.
- Direct Diode Lasers: These lasers are compact, energy-efficient, and primarily used for thin metals or precision marking.
Each laser type has its own strengths, making it suitable for different applications. At Topmetalstamping, we use a range of these lasers to provide optimal results for every project, ensuring our customers receive the best possible solution for their needs.
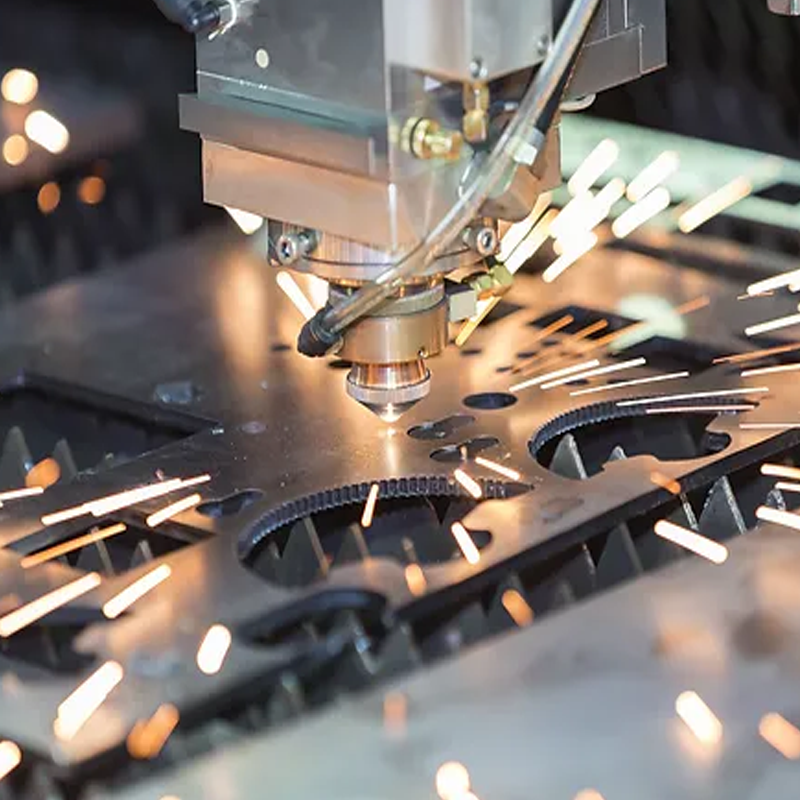

Assist Gases Used in Laser Cutting
The choice of assist gases can influence the quality and speed of the cutting process. Here are the most common gases used:
- Oxygen (O₂): Often used for cutting carbon and mild steel, oxygen enhances cutting speed but may cause oxidation along the edges. It is best for thick steel cutting.
- Nitrogen (N₂): Ideal for materials like stainless steel and aluminum, nitrogen produces cleaner cuts and prevents oxidation.
- Air: Cost-effective and ideal for cutting thin metals, plastics, and wood. Air can cause slight oxidation but is generally acceptable for many materials.
- Argon (Ar): Used for reactive metals like titanium and magnesium, argon provides excellent protection against oxidation but is more costly.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): Occasionally used as an assist gas to cut plastics, reducing discoloration or burning.
Choosing the right gas is vital to achieving the desired edge quality and cutting speed.
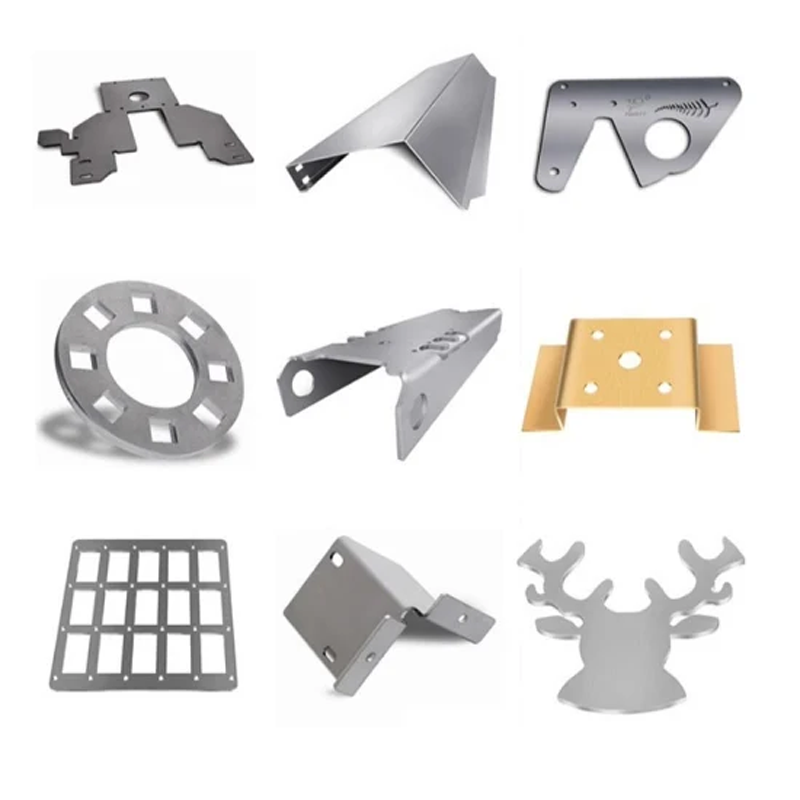

Design Tips for Laser Cutting
To ensure that your design translates well into a laser-cut part, consider the following tips:
- Material and Thickness: Select materials compatible with your laser cutting machine’s capabilities. Ensure the material’s thickness is within the supported range.
- Use Vector-Based CAD Files: Clean, precise designs in CAD software like AutoCAD or Illustrator will ensure accurate cuts. Avoid unnecessary overlapping lines.
- Kerf Width: Account for the material removed by the laser beam to avoid issues with tight-fitting or interlocking parts.
- Optimize Cut Paths: Arrange parts efficiently on the material to reduce unnecessary travel and optimize cutting time.
- Secure Material: Ensure that the workpiece is flat and well-secured to prevent issues with the laser focus and uneven cutting.
Alternatives to Laser Cutting
While laser cutting offers high precision, it is not always the best choice for every material or application. Other methods include:
- Plasma Cutting: Best for cutting thick metals quickly at a lower cost.
- Waterjet Cutting: Uses high-pressure water to cut almost any material, making it ideal for heat-sensitive parts.
- Mechanical Cutting: Includes methods like CNC routing and milling, offering flexibility but requiring tool maintenance.
- Die Cutting: Best for high-volume production of paper, leather, or thin plastics.
- EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining): Ideal for precise cuts in hard metals or small features, but slower than laser cutting.
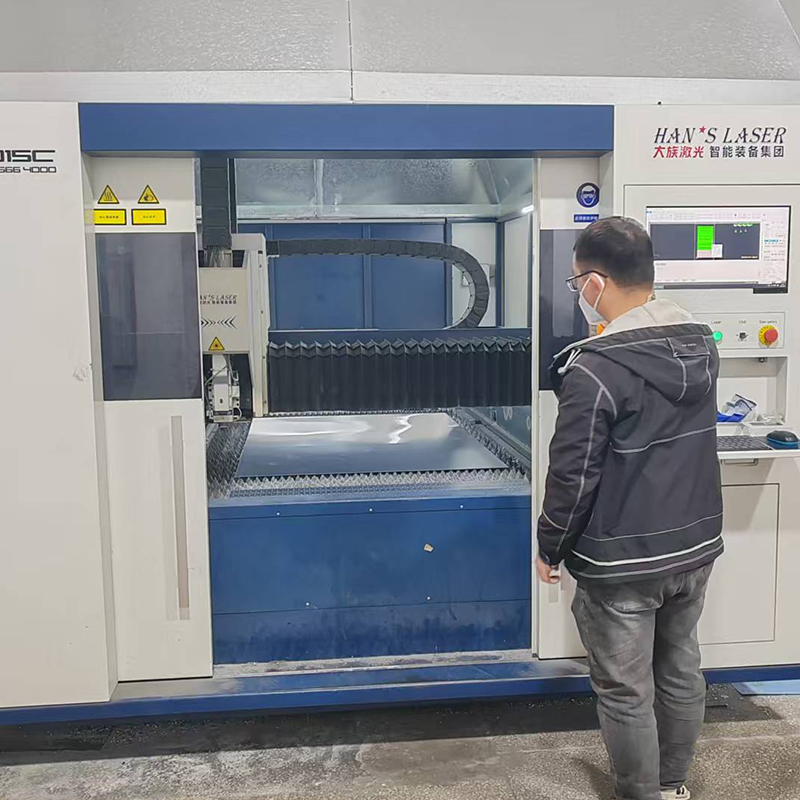

Conclusion: How Laser Cutting Benefits Your Business
Laser cutting has become a crucial technology in modern manufacturing, offering speed, precision, and efficiency across a wide range of industries. Whether you need to cut metals, plastics, wood, or composites, laser cutting delivers consistent, high-quality results with minimal waste. By understanding the key principles and choosing the right laser cutting method, you can achieve optimal outcomes for your projects.
At Topmetalstamping, we are committed to delivering high-quality laser cutting services. Our state-of-the-art laser systems and extensive manufacturing experience ensure that your projects are completed efficiently and at scale. As a leading supplier and manufacturer based in China, we are ready to help you turn your designs into precision-cut parts, meeting all your specifications and production needs.
Looking for a reliable partner in laser fabrication? Contact Topmetalstamping today to discuss your next project and see how we can support your manufacturing goals. Let us help you achieve your production objectives with the precision and quality you expect.